The Internets are all abuzz still following the kickoff this past Sunday of the third season of HBO’s flagship series Game of Thrones. There was a great deal of online anticipation in the weeks, days, and hours leading up to the season premiere, fed in part by a set of trailers (above, as well as here and here, for example) that circulated on Youtube, in the twitterverse, and beyond. And following the actual airing of the show, records were allegedly set for the most illegal downloads of a television episode, while discussions, analyses, and reviews continue to proliferate across fan sites, blogs, and news media.
(As a preliminary note to those who are either weary of reading such pieces or who are avoiding them due to spoilers — fear not: this post is neither concerned directly with the latest episode, nor will I give away anything that could ruin it for anyone who hasn’t seen it.)
Instead, I wanted to take the opportunity to comment on an aspect of the series that I’ve been thinking about (and which I recently wrote about in the more general terms of serial complexity and affect theory as applied to contemporary television). Specifically, Game of Thrones derives much of its momentum, I think, from an interplay between a continuing, complex narrative (in Jason Mittell’s sense of “narrative complexity”) and relatively discontinuous, punctuating moments of affective appeal — a directly corporeal, often visceral, sort of appeal that constitutes momentary “lines of flight” from the story’s ongoing line of development. Like much of HBO’s serial fare, these moments of affect often concern violent and/or sexualized body images which, while not completely devoid of narrative relevance, also exhibit a sort of surplus value as images. In other words, they not only serve the representational functions of depicting significant events and contributing meaningfully to characterization, etc.; over and above that, they also assert a strong presentational and extra- or para-narrational facet, the function of which is to engage the viewer’s body more than his or her interpreting, cognizing brain. Such body images — for example, in narratively gratuitous sex scenes, images of painful injury, torture, or beheading — resonate with the viewer’s own bodily sensibilities, serving to titillate or to arouse a sense of physical vulnerability, anguish, panic, or disgust.
Seen from afar (so to speak), in the overall context of a television series like Game of Thrones, the interplay between narrative development and these moments of bodily affectivity results in what I have described as a “contrapuntal” relation between the two: narrative continuity is punctuated, interrupted by body images that exceed any dramatic motivation, thus constituting more or less insular, episodic forms in the midst of the serial stream; but these islands of affect are (at least potentially) themselves elements in a serial progression that exists in parallel to that of the narrative (and following a very different temporal logic). Repetition and variation of body spectacles can thus be just as important as narrative suspense as a means of ensuring viewer attachment over the course of long serial arcs.
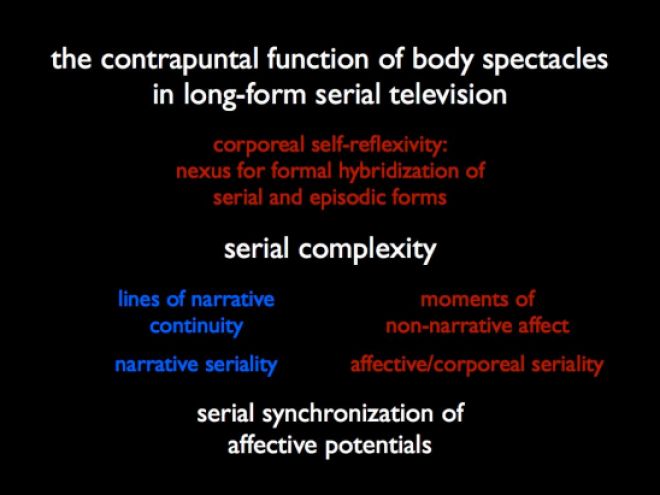
Of course, some series are more successful than others in their employment of such contrapuntal seriality, and there are certainly a wide variety of styles and modes of implementing the counterpoint. Some series are anything but discreet as they shift gears between narrative and body-based affective appeals (and in this regard, they resemble musicals or pornographic films as they move from one more or less self-enclosed “number” to the next). And certainly, some of this can be seen in Game of Thrones, but my overall impression of the series is that it works with a relatively tight integration of affective and corporeally self-reflexive appeals into the informationally complex storyworld and the unfolding tale of rival houses, subtle intrigue, and uncertain outcomes.
A particularly poignant example of contrapuntal integration is provided by episode 7 of season 1, “You Win or You Die,” where we see the following conversation between Jamie and Tywin Lannister:
Set in any other situation, this conversation — which neatly exemplifies the informational complexity of the series — would have a completely different impact. Sarah Hughes, writing in The Guardian‘s TV & Radio Blog, sees the “skinning and disembowelling [of] a deer” here as a “heavy-handed bit of symbolism given the deer is the sign of [rival] House Baratheon,” and I think she’s right to see the visual component of the scene enacting a layer of complexity beyond the content of the verbal. It’s not only a symbolic dimension, though, that is here overlaid upon the Lannisters’ discourse; in addition, I suggest, a dimension of visceral and dermic appeal spreads itself out as the very milieu within which the characters’ words sound out materially. The innards of the deer are more than just a sign: they are matter, and their material image transmits an affective force, establishing a material relation with our own viscera. The forceful separation of the animal’s skin from its muscles emphasizes, moreover, both the stubborn durability and the ultimate finitude of the organic body, arousing a diffuse affective awareness of the corporeal basis upon which our discursive subjectivities are erected. And all the while, royal politics are being discussed in detailed, lofty, and eloquent language. The scene conveys a sense of the unconscious drives that lend momentum to conscious pursuits and political “plots,” conveys a sense of the base and physical “will to power” animating social conflict. And it communicates this “message” by way of a tight contrapuntal integration of narrative information and bodily affect, thus self-reflexively exemplifying the series’ own larger strategy of instrumentalizing affect, infusing the complex (at times, overly complex) narrative with an appeal to animal nature, and in this way crafting a form of serial complexity that partakes equally of the discursive and affective.

