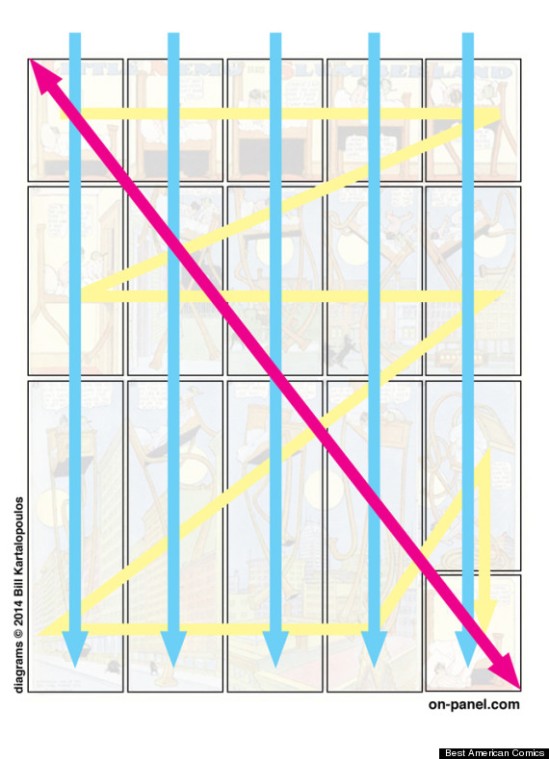
Over at Huffington Post, Bill Kartalopoulos has an interesting article on “Why Comics are More Important than Ever” (from whence the image above is taken). I highly recommend reading the piece in full, as it offers a clear, concise, and nicely illustrated exposition of some of the core medial properties of comics, along with an argument about comics’ liminal or transitional position between print and digital media.
The upshot of Kartalopoulos’s argument, which I find quite convincing, is that comics can (or do) serve us as mediators in negotiating some of the shifts and uncertainties we experience in a world that is still undergoing large-scale digitalization — but which is not destined to become digital-only. In other words, pre-digital forms are not going away; there is no “manifest destiny” of the digital, and so we must learn to navigate between medial forms that exhibit very different affordances and demands. Comics marry aspects of both forms, so that they might be seen as privileged mediators of the contemporary (and future) media landscape. As Kartalopoulos puts it:
For more than a century, comics have demonstrated a form of communication that marries the linear sequence of typography with the global perception of an internet-like matrix of simultaneous parts. […]. As we struggle within the cognitive tug of war of our new media landscape, comics offer a useful model for a new type of reading: one that might help resolve the tensions of the current media age to move us toward new productive modes of expression and understanding.
This resonates with an argument I have made regarding the serial properties of the medium — particularly with respect to what Thierry Groensteen calls the “restrained” and “general arthrology” of the comics form: the articulations or linkages that, respectively, work to unite elements in either a linear, sequential dynamics of panel-to-panel transitions or through nonlinear, networked relations between distant panels.
I have touched on these topics in “Framing, Unframing, Reframing,” my afterword to Transnational Perspectives on Graphic Narratives. What I don’t explore in that piece, but which I had in mind when writing it, was the transitional and mediating position between digital and print forms that Kartalopoulos ascribes to comics. In the hopes that it adds something useful to the discussion, and since I’ve never published it anywhere, I offer here the concluding paragraph of a talk, called “Multistable Frames: Notes Towards a (Post-)Phenomenological Approach to Comics,” which I gave in October 2011 at a conference in Bern, Switzerland:
So effectively, what I am proposing here, in the name of a phenomenological approach, is an expansion of the general arthrology developed by Groensteen, who notes that the narrative operations of comics take root in linear sequences of contiguous panels but give rise to braidings or translinear series that establish themselves between distant panels. By following these braided networks beyond the diegesis, beyond the work, and into a plurimedial field of connectivities and the lifeworld it structures, we can appreciate the truth of a remark that Groensteen makes in the conclusion of his book. There, he writes: “comics, which marries the visual and the verbal, demonstrates a discontinuity, a staggering, and the effects of networks, and finally constitutes a sort of image bank, appear to be situated not far from the turning point between the civilization of the book and that of multimedia” (160). We can say, then, that comics are transitional between old and new media due to the emergent seriality that proliferates as a result of comics’ nested multistabilites, a seriality that Groensteen describes as a “supplementary relation” that is “inscribed like an addition that the text secretes beyond its surface” (146-147). Always vacillating between the linear narrative sequence and the translinear network, comics define their seriality as a space of the in-between: between self-enclosed books on the one hand and the total network of hypertext and convergent digital media on the other. As this in-between space of serial proliferation, comics are not assimilable to the monomedial narration of the book, and they resist as well the higher-level closure of transmedial storytelling while upsetting the exhaustive cataloguing projects of digital databases and wikis. With their plurimedial seriality, comics remain squarely in-between. With their techniques of retcon and reboot, for example, and more generally the fact of multistable framing at every level, proliferating in an unruly seriality, comics can be said to have set the stage for a consideration of the experiential gaps between old and new media. As a truly transitional medium, comics inherently confound every attempt at closure or totalization—both the self-contained book and the encyclopedic database depend on discrete categories that are incapable of accommodating the ambiguity and plurality of the multistable frame. And so, despite appearances that they might settle down, let themselves be tamed according to book-centric categories of “respectable” literature—as graphic novels—or captured and rendered coherent and manageable in the convergent space of the digital, comics remain elusive, on the move, and productive of a self-serializing dynamics of the transition. In this respect, they may be useful for understanding the parameters of a rapidly changing visual culture.